During my five years with Global Founders Capital, Rocket Internet’s $1 billion VC arm, I saw more than a hundred of Rocket’s incubated companies attempt to internationalize. For background, Rocket Internet has helped launch some very successful businesses internationally, including HelloFresh ($12.9 billion market cap), Lazada ($1 billion exit to Alibaba), Jumia ($3.2 billion market cap), Zalando ($21.2 billion market cap) and many others. Rocket often followed the Blitzscaling model popularized by Reid Hoffman — earning them an appearance in his book of the same name.
After an initial success helping Groupon scale internationally via a merger with Rocket’s incubation firm CityDeal, Rocket’s team have aggressively scaled businesses from Algeria to Zimbabwe — sometimes in a matter of weeks. No surprise, Rocket also has a graveyard of failed companies that were victims of bad internationalization efforts.
Many companies make the costly mistake of launching abroad too soon.
My personal observations on Rocket’s successes and failures start with this crucial point: These learnings might not apply to your unique combination business model, market and timing. No matter how well you prepare and plan your internationalization, in the end you need to be agile, alert and smart as you dip your toes into your first foreign market.
Fail fast and cheaply
Internationalization can be a big driver of growth and consequently enterprise value, which is why investors always push for it. But going abroad can also destroy value just as quickly. As a founder, it’s your job to manage financial and operational risks. Finding the right balance between keeping costs in check and not underinvesting can mean doing things more slowly than your board would like. For example, you might launch new markets sequentially instead of rolling 10 out at the same time.
Adopt a “hire slow, fire fast” mentality for your expansion strategy. Don’t be afraid to pull the plug if things don’t work out.
Our team at Heartcore Capital use the following framework and learnings to guide internationalization strategies for our portfolio companies. A successful internationalization strategy needs to answer and address the “Four Ws”: When, Where, Which and With whom to internationalize. (Regarding the fifth W from journalism, you should not need to ask the “Why” question if you want to build a large business!)
1. When is the right time to start?
Many companies make the costly mistake of launching abroad too soon. They look at internationalization as a detached function, isolated from the rest of the business and then launch their second market prematurely. Follow this simple rule: Wait to internationalize until you hit product/market fit.
How do you know exactly when you’ve reached product/market fit? According to Marc Andreessen, “Product/market fit means being in a good market with a product that can satisfy that market.” He adds that experienced entrepreneurs can usually feel if they’ve reached this point.
Let’s take the man for his word and move on to the actual argument: Until you have product/market fit, you will not be able to distinguish between what you’ve learned from your business model and what you’ve learned from your in-country experience. Mistakes will compound. Complexities and costs will multiply. I contend that insufficient understanding of their business and operating model is the main reason why companies fail with their expansion strategies.
Founders should also consider the underlying costs of internationalizing before they decide to expand (more about this in the “What” section below). Some companies are global by default — think mobile gaming companies — or simply require language localization. Others need to build new warehouses, hire local teams or build entirely new products. The costs and respective risks of expanding prematurely depend heavily on the business model.
There are edge cases where companies need to move quickly to internationalize for strategic reasons — despite uncertainty about their market fit. For instance, companies like Groupon or those engaged in food delivery face winner-takes-most markets, where opportunities for product differentiation are limited. “Blitzscaling” makes sense in cases like these.
However, you should tread carefully if your only reason to start scaling abroad is a large fundraise or to match a competitor’s internationalization efforts. Scaling prematurely for the wrong reasons might just cost you your entire company.
When Rocket Internet announced it would launch the Homejoy model into European markets with Helpling, the American “original” company launched quickly in Germany in an effort to squash their new competitor. In the early days of “on-demand everything,” a managed marketplace for cleaning services sounded like the next unicorn in the making.
In 2013, Homejoy had a fresh $24 million Series A from Google Ventures and First Round — considered a huge round at a time when Instacart had just raised an $8 million Series A and Snapchat had done a $13 million Series A round. It must have seemed like a good idea to squash the German competition early.
As it turned out, Homejoy’s product was not yet ready to scale internationally. Just 13 months after launching in Germany, Homejoy had to cease operations globally, while Rocket’s Helpling is still alive and kicking. Helpling focused carefully on product, automation and making their unit economics work. A rush to crush an international competitor caused the demise of a would-be unicorn.
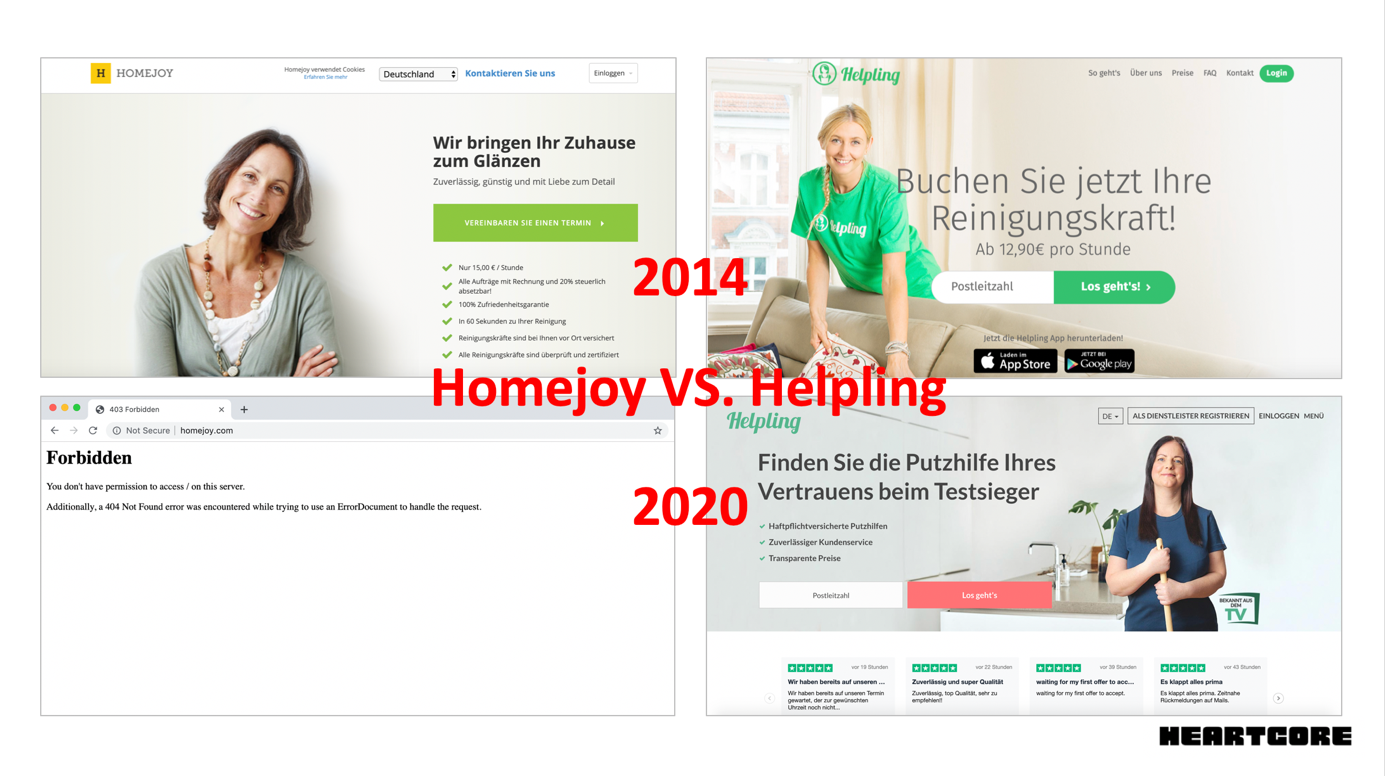
Homejoy expanded internationally in 2014 in a rush to squash a new German competitor Helpling. Their websites in 2020 show starkly different outcomes. Image Credits: Homejoy/Helpling
2. Where should you internationalize?
When deciding which new international market to tackle, it is vital to do your homework. Analyze the competitive environment, partner availability, infrastructure, culture, regulation and synergies with your home market.
In the early days of e-commerce, it was rather easy to analyze if a market was an expansion target. In the absence of professional competition, Rocket chose new countries based solely on GDP and internet penetration.
from Startups – TechCrunch https://ift.tt/3mSz5Vh
Comments
Post a Comment