Robotic process automation platform UiPath added its name to the list of companies pursuing public-market offerings this morning with the release of its S-1 filing. The document details a quickly growing software company with sharply improving profitability performance. The company also flipped from cash burn to cash generation on both an operating and free-cash-flow basis in its most recent fiscal year.
Companies that produce robotic process automation (RPA) software help enterprises reduce labor costs and errors. Instead of having a human perform repetitive tasks like data entry, processing credit card applications and scheduling cable installation appointments, RPA tools employ software bots instead.
The phrase that matters most when digesting this IPO filing is operating leverage, what Investopedia defines as “the degree to which a firm or project can increase operating income by increasing revenue.” In simpler terms, we can think of operating leverage as how quickly a company can boost profitability by growing its revenue.
The greater a company’s operating leverage, the more profitable it becomes as it grows its top line; in contrast, companies that see their profitability profile erode as their revenue scales have poor operating leverage.
Among early-stage companies in growth mode, losing money is not a sin — after all, startups raise capital to deploy it, often making their near-term financial results a bit wonky from a traditionalist perspective. But for later-stage companies, the ability to demonstrate operating leverage is a great way to indicate future profitability, or at least future cash-flow generation.
So, the UiPath S-1 filing is at once an interesting picture of a company growing quickly while reducing its deficits rapidly, and a look at what a high-growth company can do to show investors that it will, at some point, generate unadjusted net income.
There are caveats, however: UiPath had some particular cost declines in its most recent fiscal year that make its profitability picture a bit rosier than it otherwise might have proven, thanks to the COVID-19 pandemic. This morning, now that we’ve looked at the big numbers, let’s dig in a bit deeper and learn whether UiPath is as strong in operating leverage terms as a casual observer of its filing might guess.
And then we’ll dig into four other things that stuck out from its IPO filing. Into the data!
Operating leverage, cost control and COVID-19
To avoid forcing you to flip between the filing and this piece, here’s UiPath’s income statement for its fiscal years that roughly correlate to calendar 2019 and calendar 2020: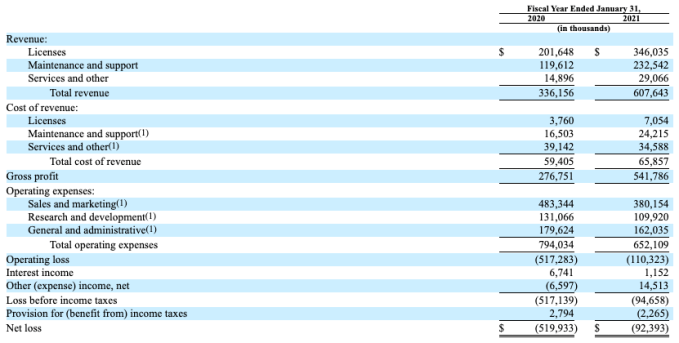
From top-down, it’s clear UiPath is growing rapidly. And we can see that its gross profit grew more quickly than its overall revenue in its most recent 12-month period. As you can imagine, that combination led to rising gross margins at the company, from 82% in its fiscal year ending January 31, 2020, to 89% in its next fiscal year.
That’s super good, frankly; given that UiPath has a number of business lines, including a services effort that doubled in size during its most recent 12 months of operations, you might expect its blended gross margins to fade. They did not.
But it’s the following section, the company’s cost profile, that leads us to our first real takeaway from the UiPath S-1:
UiPath’s operating leverage looks good, even if COVID helped
Every operating expense category at the company fell from the preceding fiscal year to its most recent. That’s an impressive result, and one that is key when it comes to understanding where UiPath’s recent operating leverage came from. But how the declines came to be is just as important to understand.
from Startups – TechCrunch https://ift.tt/3rlJ1Zz
Comments
Post a Comment