Apple has some of the strictest rules to prevent malicious software from landing in its app store, even if on occasion a bad app slips through the net. But last year Apple took its toughest approach yet by requiring developers to submit their apps for security checks in order to run on millions of Macs unhindered.
The process, which Apple calls “notarization,” scans an app for security issues and malicious content. If approved, the Mac’s in-built security screening software, Gatekeeper, allows the app to run. Apps that don’t pass the security sniff test are denied, and are blocked from running.
But security researchers say they have found the first Mac malware inadvertently notarized by Apple.
Peter Dantini, working with Patrick Wardle, a well-known Mac security researcher, found a malware campaign disguised as an Adobe Flash installer. These campaigns are common and have been around for years — even if Flash is rarely used these days — and most run unnotarized code, which Macs block immediately when opened.
But Dantini and Wardle found that one malicious Flash installer had code notarized by Apple and would run on Macs.
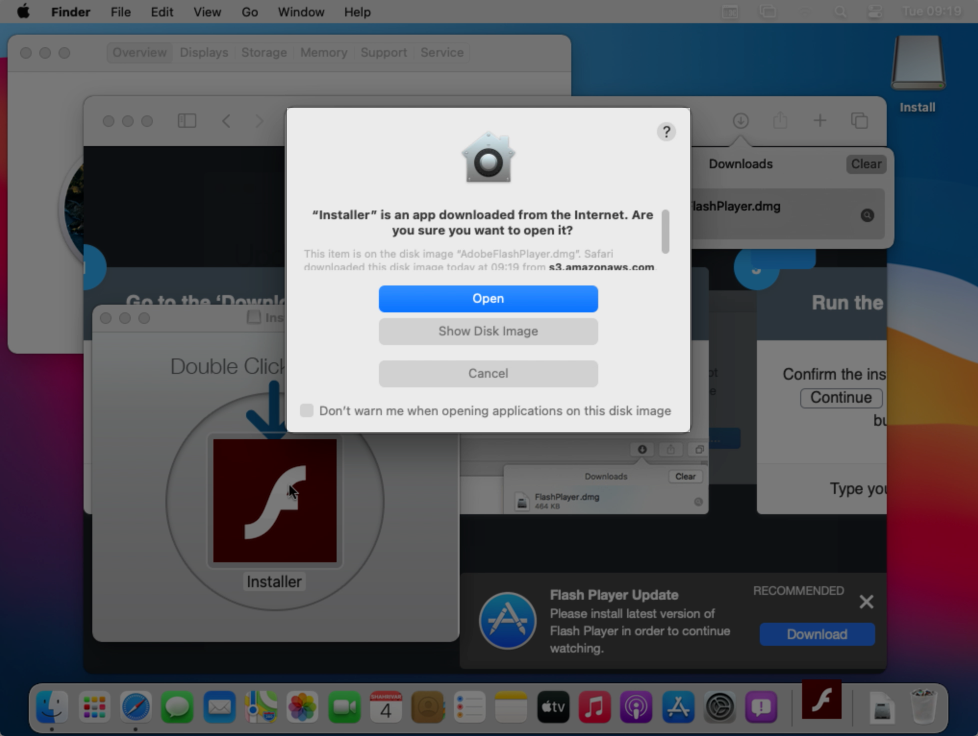
The malicious installer was notarized by Apple, and could be run on the latest versions of macOS. (Image: Patrick Wardle/supplied)
Wardle confirmed that Apple had approved code used by the popular Shlayer malware, which security firm Kaspersky said is the “most common threat” that Macs faced in 2019. Shlayer is a kind of adware that intercepts encrypted web traffic — even from HTTPS-enabled sites — and replaces websites and search results with its own ads, making fraudulent ad money for the operators.
“As far as I know, this is a first,” Wardle wrote in a blog post, shared with TechCrunch.
Wardle said that means Apple did not detect the malicious code when it was submitted and approved it to run on Macs — even on the unreleased beta version of macOS Big Sur, expected out later this year.
Apple revoked the notarized payloads after Wardle reached out, preventing the malware from running on Macs in the future.
In a statement, a spokesperson for Apple told TechCrunch: “Malicious software constantly changes, and Apple’s notarization system helps us keep malware off the Mac and allow us to respond quickly when it’s discovered. Upon learning of this adware, we revoked the identified variant, disabled the developer account, and revoked the associated certificates. We thank the researchers for their assistance in keeping our users safe.”
But Wardle said that the attackers were back soon after with a new, notarized payload, able to circumvent the Mac’s security all over again.
from Apple – TechCrunch https://ift.tt/3lCeJ35
Comments
Post a Comment