After years of fierce competition as private companies, Uber and Lyft are going public on U.S. markets. Scooter service providers, the transportation trend du jour, raised hundreds of millions of dollars to scatter scooters on city sidewalks (to the chagrin of residents and regulators alike) throughout 2017 and 2018. On the other side of the Pacific, Grab and Go-Jek are raising gobs of cash as they continue to scale upward and outward.
Of all the seed, early and late-stage venture funding raised over the past couple of years, how much of the total went to companies in the ride-hailing, food delivery and last-mile transportation categories (which encompasses bikes and scooters)? Probably not as much as you’d think.
Taken together, companies in these sectors raised less than 10 percent of the total venture dollar volume reported for each of the past five full calendar years.
We’ve charted it out based on yearly totals. Take a peek:
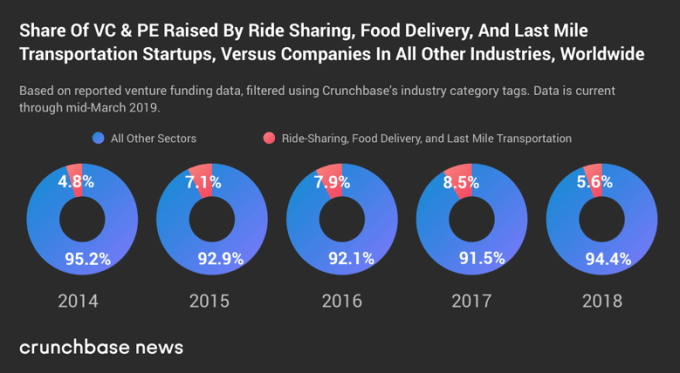
To be sure, we’re still talking about a lot of money here. Companies in these three categories raised more than $22 billion in venture funding rounds (not including private equity) in 2017 and more than $18 billion in 2018.
Ventures in the transportation space loom large in the media, and how could they not? It’s a forbiddingly capital-intensive market to play in, requiring companies to raise massive sums, which make for good headlines.
In its early years, competition between on-demand, point-to-point transportation marketplace companies rewarded brashness and speed with early scale and the long-term structural advantages conferred to first the firms which grew the fastest.
But those advantages may not have been as stiff as first expected. Lyft beat Uber to the public markets, raised its valuation during its IPO roadshow, priced at the top of its extended range and then popped 21 percent when it started trading.
That success means that the red chunks of our above chart weren’t all fool’s bets. Instead, a good chunk of the equity represented is now liquid. Of course, there’s a lot more work to do for literally every other ride-hailing, ridesharing, scooter-renting and other wheels-providing unicorns in the world: They still have to go public.
from Startups – TechCrunch https://ift.tt/2FMlE77
Comments
Post a Comment